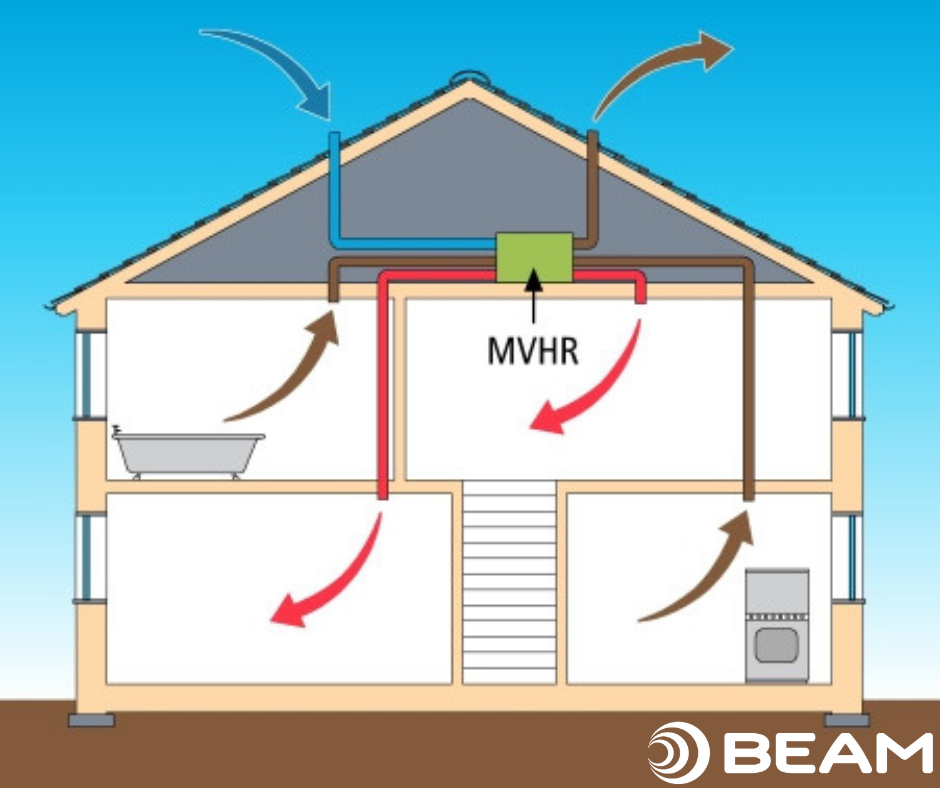
Manual ventilation and MVR
Manual ventilation and mechanical ventilation with heat recovery (MVHR) are two different approaches to providing fresh air in buildings. While both methods serve the same purpose of improving indoor air quality, they have distinct differences that are worth exploring.
Manual ventilation refers to the process of opening windows or using portable fans to bring fresh air into a space and remove stale air. This method has been used for centuries and relies on natural airflow to provide ventilation. It is a simple and cost-effective solution that does not require any complex installations or mechanical systems. Manual ventilation is commonly used in residential buildings, small offices, and other spaces where the occupancy and ventilation needs are relatively low.
While manual ventilation is easy to implement, it has limitations. The effectiveness of manual ventilation depends on factors such as external weather conditions, proximity to pollution sources, and the ability to maintain a balance between ventilation and energy efficiency. Additionally, manual ventilation does not offer any heat recovery capabilities, meaning that the energy used to heat or cool the indoor space is lost when air is exchanged with the outside atmosphere.
On the other hand, mechanical ventilation with heat recovery (MVHR) is a more advanced and efficient method of providing fresh air. MVHR systems use fans and ducts to distribute fresh air throughout the building while simultaneously extracting stale air. This process not only improves indoor air quality but also helps conserve energy.
The key feature of MVHR systems is the incorporation of heat recovery units. These units transfer heat from the extracted air to the incoming fresh air, reducing the amount of energy required to heat or cool the incoming air stream. As a result, MVHR systems can significantly improve energy efficiency, reduce heating and cooling costs, and provide a more comfortable indoor environment.
MVHR systems are particularly beneficial in buildings with higher occupancy, such as large offices, schools, hospitals, and apartment complexes. The ability to recover heat from outgoing air reduces the dependency on mechanical heating and cooling systems, leading to reduced energy consumption and lower carbon emissions.
In conclusion, both manual ventilation and mechanical ventilation with heat recovery have their advantages and are suitable for different scenarios. Manual ventilation is a simple and cost-effective option for smaller spaces with relatively low occupancy, while MVHR systems provide enhanced ventilation and energy efficiency benefits, making them ideal for larger residential and commercial buildings. Choosing the appropriate ventilation method depends on factors such as occupancy, building size, climate, and energy requirements. Consulting with a professional HVAC engineer can help determine the most suitable ventilation solution for a specific building.